Robots near carpe diem moment


First impressions, they say, leave deep impressions. How true!
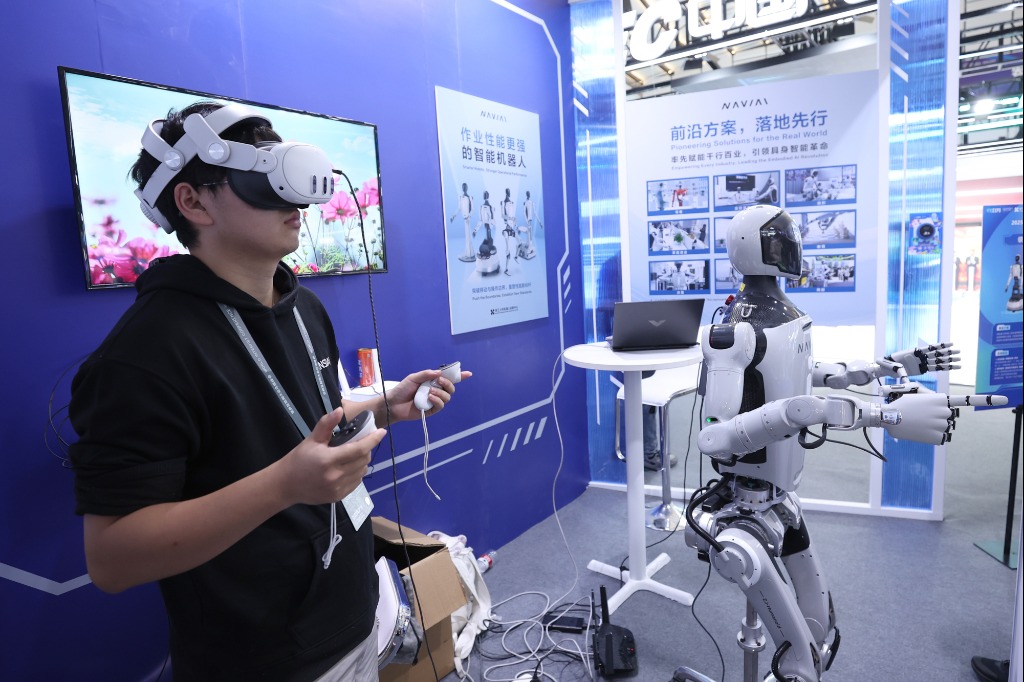
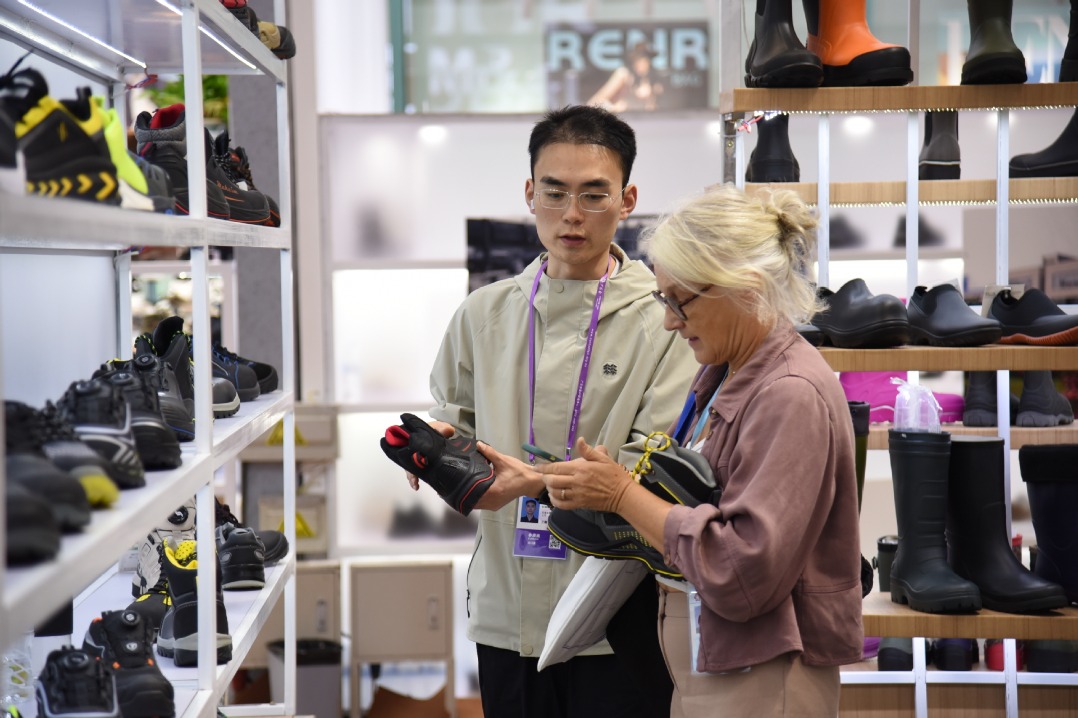
I had my first experience of robots at the 19th China International Industry Fair in Shanghai earlier this month. And the devices have created such deep crevices in my mind that a dichotomy, an inner conflict of sorts, is forming.
I can't stop thinking about those various types of industrial and service robots-how they are versatile enough to perform wide-ranging functions such as folding a shirt, mixing cocktails and welding.
And they left me paranoid. Would bionic robots grab my job one day in the not-so-distant future, leaving me jobless, unemployable, redundant?
You'll see shortly my fears are not completely unfounded. I learn European and Japanese manufacturers have already begun producing more service robots in China to keep up with growing demand.
Rising middle-class affluence and urbanization are spawning intense demand for a variety of services, which is causing worker shortages in many service and labor-intensive industries. The problem is aggravated by high attrition rates and rising cost of labor.
Worse, millions of migrant workers have returned to their homes in the countryside or lower-tier cities in recent years, unable to cope with the transition pressures exerted by factors like high cost of living. But many are staying put in the hope of finding work in mega cities.
This trend is coinciding with manufacturing as well as consumption upgrades in China, which is marked by frenetic efforts to boost industrial output. The automotive, chemical, communication and consumer electronics sectors have been among the hardest hit by this rush.
There is growing pressure on companies to increase their investment to fully automate factories. They call it "intelligent manufacturing".
New-age robots can deliver multiple services, from cleaning and assembly operations in the chemical and automotive sectors to working at unimaginable heights or depths where human workers face safety risks.
The countrywide reach of the robotics revolution and the shrinking rural workforce appear to be two sides of the same coin.
For Chinese manufacturers, it seems, low production levels, rising labor costs, outdated management methods and changing demographics are desperate challenges that need to be dealt with forthwith, before they morph into a crisis. So, they are pushing hard toward putting robots to work at their factories, plants and R&D facilities.
By the way, the metal-and-synthetic molds with embedded circuitry and software are seen as, well, more reliable, more efficient, more productive and more versatile than human workers.
You'll probably agree with me by now that my growing paranoid streak is not misplaced.
But then, is China's industrial robot industry ready for a massive robot job takeover, which appears almost inevitable now?
The industry is far from mature. It's still nascent in terms of independent innovation, and manufacture of core components as well as complete sets of robots. Domestic robot firms rely heavily on imports and collaborations with foreign companies.
They have to for now, because they are keen to equip their factories with industrial robots to improve efficiency and accuracy. Home-made robots are not for the high-end market anyway.
Foreign firms hold an 80 to 90 percent market share in robots capable of sophisticated maneuvers, while China-made robots are mainly used for simple operations such as carrying, arranging and material handling.
According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, there are now more than 800 robot manufacturers in China, of which 200 produce the main bodies while the others are mainly engaged in assembly or material processing.
Three major components of industrial robots-sensors, speed reducers and servo motors-are still in the firm grip of foreign firms. This means, Chinese robot manufacturers have little bargaining power to influence product prices.
The dichotomy to deal with now therefore is this: should the local industry continue the current pattern of deploying more and more robots to perform jobs that were earlier done by human workers? Or, given the huge domestic market, should it cry carpe diem, seize the moment, and decisively shift its attention to becoming more capable of independent innovation?