Sci-tech helps protect South China biological treasure trove


GUANGZHOU -- In the early 1880s, an American discovered a beautiful and mysterious flower on a cliff close to the Lianjiang River in northern Guangdong province, South China. Later, a British botanist published research done on this flower.
However, for over a century after its discovery, no one saw this flower again. Named Primulina tabacum, it was once believed to be extinct.
It was not until the 1990s that the flower was rediscovered in Lianzhou, Guangdong. At that time, only three surviving plants were documented, and it was classified as critically endangered. This species typically inhabits specific microhabitats in the karst caves of southern China, where its survival faces severe threats.
In 2002, researchers from the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences launched an ex-situ conservation program for Primulina tabacum.
They discovered that the plant grows on limestone cave cliffs with high carbon dioxide concentrations and does not require bees for pollination. Further studies revealed that when its petals fall, they trigger collisions between stamens and pistils, enabling self-pollination.
Notably, scientists have successfully applied cloning technology to cultivate this plant — mastering rapid propagation techniques and reintroducing about 3,000 individuals into the wild.
Currently, the SCBG has conserved 1,050 rare and endangered plant species, including 558 state-protected wild plants. Its dedicated rare and endangered plant breeding center spans 20 hectares and houses over 230 such species, making it one of China's largest germplasm banks for rare flora.
The botanical garden aims to ensure effective protection of 95 percent of south China's rare and endangered plants, and to reintroduce 20 species into their natural habitats.
"We protect each plant not because of its known value, but because we don't know its potential importance yet. With so few wild individuals left, conservation is imperative. Once a species vanishes, it's gone forever," said Ning Zulin, deputy director of the garden's horticulture center.
AI ASSISTANCE
How many species exist on Earth? There remains no definitive answer. Historically, documenting and studying biodiversity relied on experts. Now, big data and AI technologies are revolutionizing public engagement, offering new ways to record, understand and protect biodiversity.
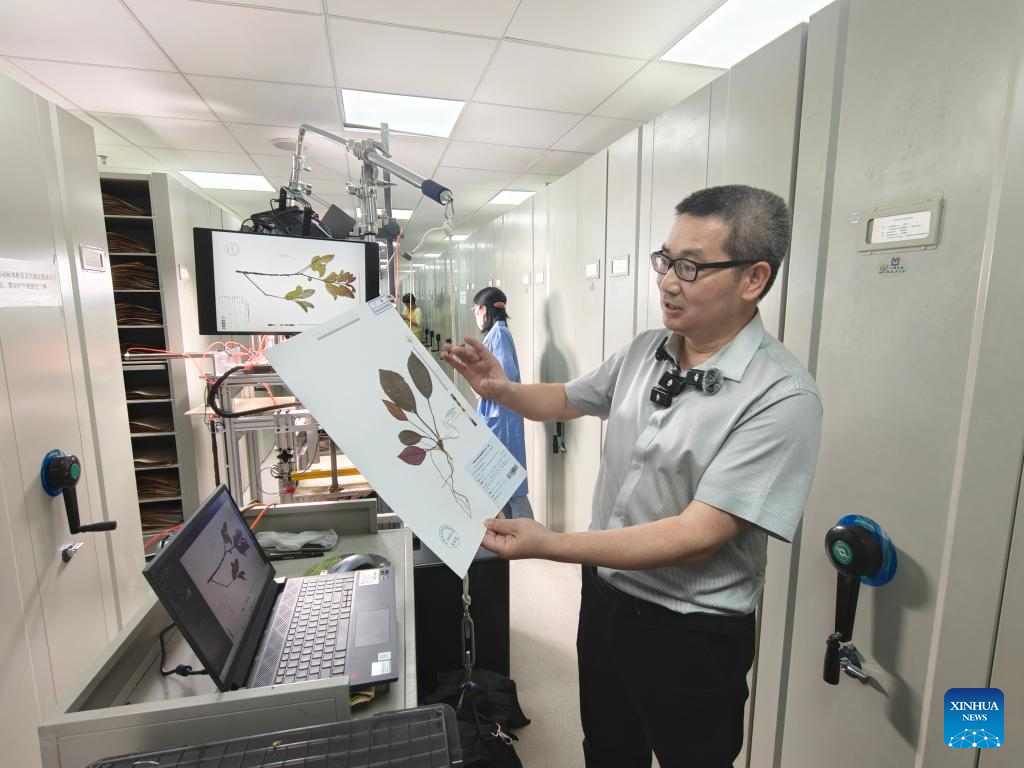
Luo Shixiao, curator of the SCBG herbarium, said through an independently developed intelligent specimen management system, named Cathaya, the herbarium in 2024 completed the reception of over 50,000 plant specimens and uploaded 300,000 pieces of spatiotemporal distribution information concerning the collected specimens. More than 250,000 pieces of specimen data were shared via the system.
This system has enabled efficient management of the entire process from field investigation to digital sharing of specimens — setting a new paradigm for biodiversity research and intelligent management.
The herbarium also developed the "BioGrid" app, a biodiversity observation and identification tool, by using large-scale scientific data and artificial intelligence. This app addresses challenges such as precise plant localization and species identification, enhancing data collection and species recognition capabilities for both professionals and the public, according to Xu Zhoufeng, an engineer at the herbarium.
The app provides data collection, project organization, data perception and visualization services for professionals, while also enabling the public to conveniently participate in biodiversity science projects, Xu said.
- Exhibition commemorating the epic relocation of universities opens in Fujian
- Twelve punished for scaffold collapse that killed 7 in Shandong
- Slovenian official visits whole-process people's democracy practice site of CPPCC committees
- China's commercial rocket maker puts two satellites into orbit
- People in Taiwan commemorate victims of White Terror period
- China successfully launches new test satellites