Pharmaceutical levies won't prompt reshoring

After imposing sweeping "reciprocal tariffs" against the world four months ago, the United States is mulling a new round of targeted sector-specific tariff attacks.
US President Donald Trump said on Tuesday that he plans to announce tariffs on semiconductors and chips in the "next week or so", and place a "small tariff" on pharmaceutical imports before hiking it to 150 percent within 18 months and eventually to 250 percent.
Although he did not specify the initial tariff rate on pharmaceuticals, Trump said in February that sectoral tariffs on pharmaceuticals and semiconductor chips would start at"25 percent or higher", rising substantially over the course of a year.
The US initiated a Section 232 investigation on pharmaceutical products in April, purportedly to verify the impact of imports on "national security". It is believed this was a prelude to the planned levies which the US leader hopes can help the US boost the domestic production of medicines.
Pharmaceutical drug production in the US has shrunk dramatically over the last few decades. In 2024, the US' trade deficit in medicines reached $139 billion out of a total goods trade deficit of $1.2 trillion. Many US pharmaceutical companies have moved their manufacturing operations to other countries, such as Ireland, due to lower labor costs and other factors. Although they seem to be contributors to the US' trade deficit, they are the major beneficiaries of the model.
But industry observers have warned that the planned tariffs, along with an executive order of the president in May, could drive up costs, deter investments in the US, affect the whole industry's research and development, and disrupt the drug supply chains, putting patients at risk. The executive order aims to slash drug costs by tying the prices of some medicines in the US to lower ones abroad.
In response to the possible resistance from pharmaceutical companies and the wide concerns about rising medical bills for US families, the US president last week sent letters to 17 drugmakers calling on them to commit to steps to lower US drug prices by Sept 29. That includes agreeing to provide their full portfolio of existing medicines at the lowest price offered in other developed nations to every single medicaid patient, among other steps. The information they are pressed to provide is expected to be used to facilitate the implementation of the aforementioned "most favored nation" policy. The US drugmakers are obviously being caught in a similar dilemma to that of US carmakers when the US raised tariffs on imported vehicles and parts.
Yet the US administration's maximum pressure tactics are already producing results. Companies such as Eli Lilly and Johnson & Johnson announced fresh US investments in the past few months, according to a CNBC report. And Reuters has reported that AstraZeneca has just committed $50 billion to expand its operations in the US.
Although the US administration seems to be leaving the companies enough time to relocate their production to the US with its planned phased tariff hikes over more than a year, to what extent the latter will comply depends on their profit-cost balance. The exorbitant 250 percent tariffs the US leader threatened, the highest for a sector so far, to some extent reflects the huge cost it will incur to shape a US-led pharmaceutical industry by reforging supply chains around the world.
The pharmaceutical industry boasts arguably one of the most sophisticated systems of global division of labor. The planned tariffs, if they materialize, will also slow down the catch-up of developing countries in the industry by realizing the US' control of their product sources and related technologies and equipment. That will certainly prompt some emerging market economies to accelerate independent innovation in the industry.
The proposed tariffs also look set to further complicate the already strained trade relations between the US and Europe. Ireland, Germany and Switzerland, which are the top three exporters of pharmaceuticals to the US, accounting for about 60 percent of the exports to the country combined, will bear the main brunt of the levies.
Just like in the chip and artificial intelligence sectors, the formation of two de facto parallel systems in the pharmaceutical sector will markedly increase R&D costs and slow the pace of technological development. Ultimately, it is ordinary people who will pay the price for the tariff hikes.
Today's Top News
- China to apply lower import tariff rates to unleash market potential
- China proves to be active and reliable mediator
- Three-party talks help to restore peace
- Huangyan coral reefs healthy, says report
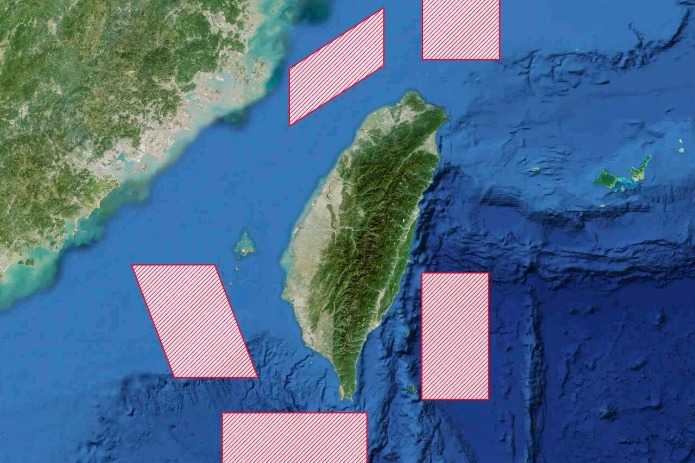
- PLA conducts major drill near Taiwan
- Washington should realize its interference in Taiwan question is a recipe it won't want to eat: China Daily editorial