High-speed rail mirror of China's modernization: China Daily editorial


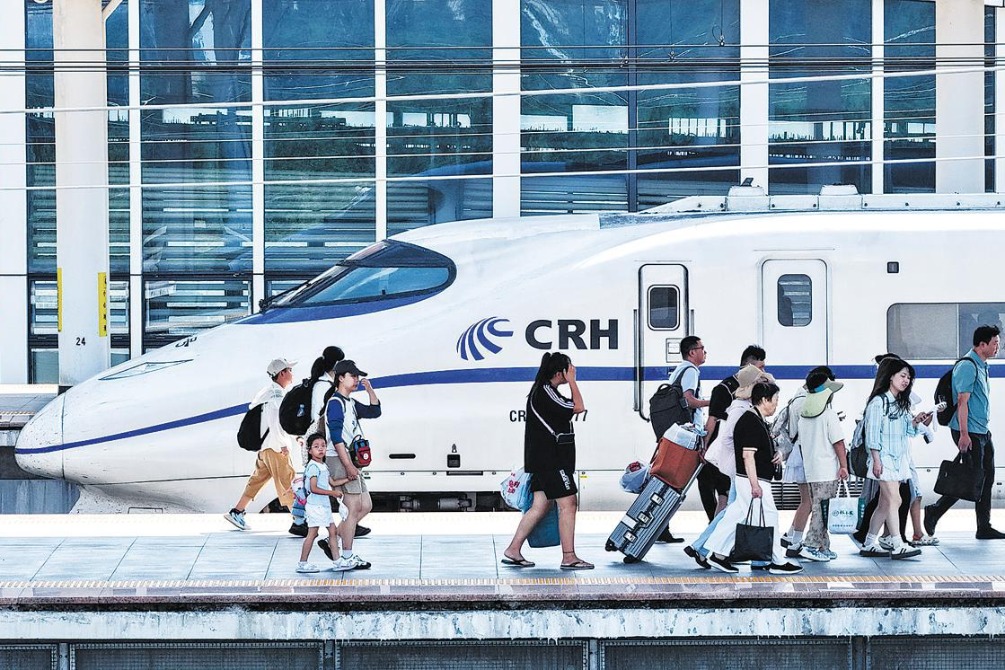
How China has changed over the past decades can be judged by the development achievements it has made. One of the most straightforward ways to appreciate that is perhaps to look at the country's network of high-speed railways.
New services commenced on four new lines — Xi'an-Yan'an, Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu, Wuhan-Yichang and Hangzhou-Quzhou — on Friday. That brings the total length of the high-speed railways in operation in the country to over 50,000 kilometers, more than the length of all the high-speed railway lines in the rest of the world put together.
The national network of high-speed railway lines now embraces 97 percent of cities with a population of more than 500,000.
Travel between cities within the radius of 500 kilometers by high-speed rail takes between one and two hours, and a trip between cities within the radius of 1,000 kilometers takes about four hours. Now the average daily number of passenger trips by high-speed railway is about 16 million.
For such a huge country where people often live and work far from their hometowns, this is more than just statistics.
When it was a headache to purchase a railway ticket during busy seasons and the average speed of the railways was just 60 kilometers per hour, no one could have imagined that just three decades later, high-speed railways with speeds of 300 km per hour or even more would make journeys not only quicker but also more convenient.
It took just four years for the total length of high-speed railways to increase from 40,000 kilometers to 50,000 kilometers during the 14th-Five-Year Plan (2021-25) period. Compared with other countries, that is remarkable. And it should be pointed out that the mileage of high-speed railways increased from 10,000 kilometers to 40,000 kilometers in China from 2013 to 2021. The development of high-speed railways has now shifted from linking the major cities to connecting the major cities with medium-sized and small cities. This effectively promotes the economic and social development of these smaller cities and towns.
Data show that in the decade from 2014 to 2024 since the high-speed railway line between Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, and Changsha, Hunan province, went into operation in 2014, the total number of tourists in Jiangxi province, which is located between Zhejiang and Hunan, had increased 248 million to reach 818 million.
In addition, the feasibility of maglev railways that can operate at up to 600 kilometers per hour is being studied for major city clusters in the years to come, which will further increase transport efficiency and promote the economic and social development of major cities.
China has also shared its knowledge and experience with other countries, cooperating with more than 40 on the development of high-speed railways, such as the Jakarta-Bandung High-Speed Railway in Indonesia, the Hungary-Serbia Railway and the China-Laos Railway. It took about three decades for China to move from importing high-speed rail technology to developing its own and exporting it, along with its expertise and standards, to other countries.
As Alan Beroud, chairman of the International Union of Railways, noted at the 12th World Congress on High-Speed Rail in Beijing in July, "In less than two decades, China has created the largest and most advanced high-speed rail system in the world. It's reshaping mobility, the economy and regional development."
During the 15th Five-Year Plan (2026-30) period, greater emphasis will be placed on the quality and efficiency of China's high-speed railways, along with optimization of the network.