Fossil finger may rewrite China's human history

Discovery could challenge years of widely-held beliefs
A fossil of a human finger found by British archaeologists in Saudi Arabia supports a theory long held by Chinese researchers that modern humans left Africa and migrated to China tens of thousands of years earlier than previously thought.
The commonly-held view in the scientific community is that early Homo sapiens first migrated from Africa to what is now Europe and the Middle East around 60,000 years ago, and reached southern China as early as 45,000 years ago.
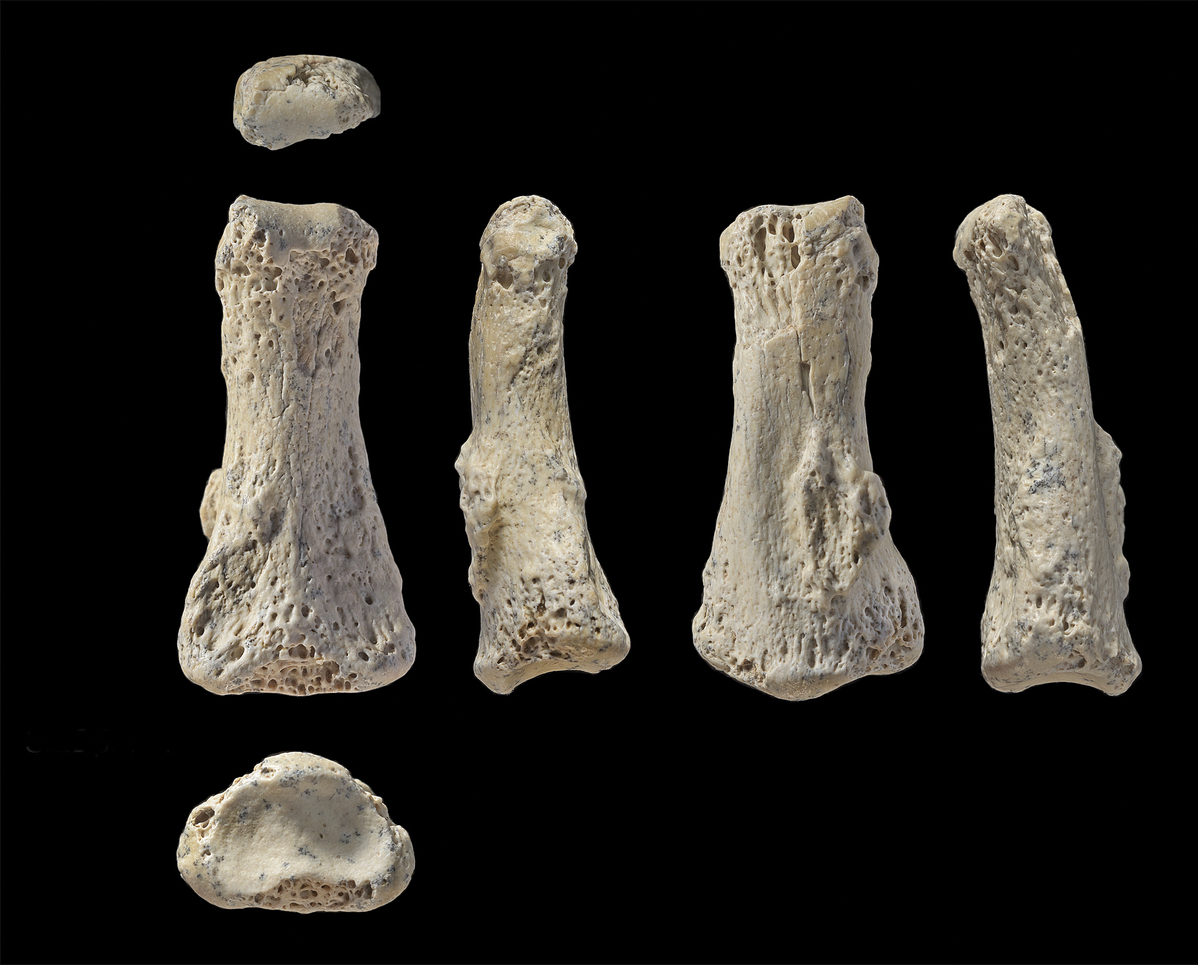
The discovery of an 88,000-year-old human finger bone at the Al Wusta archaeological site in the Nefud Desert, Saudi Arabia, has turned this idea on its head. The age of the fossil suggests an earlier migration from Africa into Eurasia - a theory supported by other archaeological discoveries made in China that were previously met with skepticism.
“It now seems likely that early modern humans were in southern China about 100,000 years ago,” said Professor Chris Stringer, who researches human origins at the Natural History Museum in London.
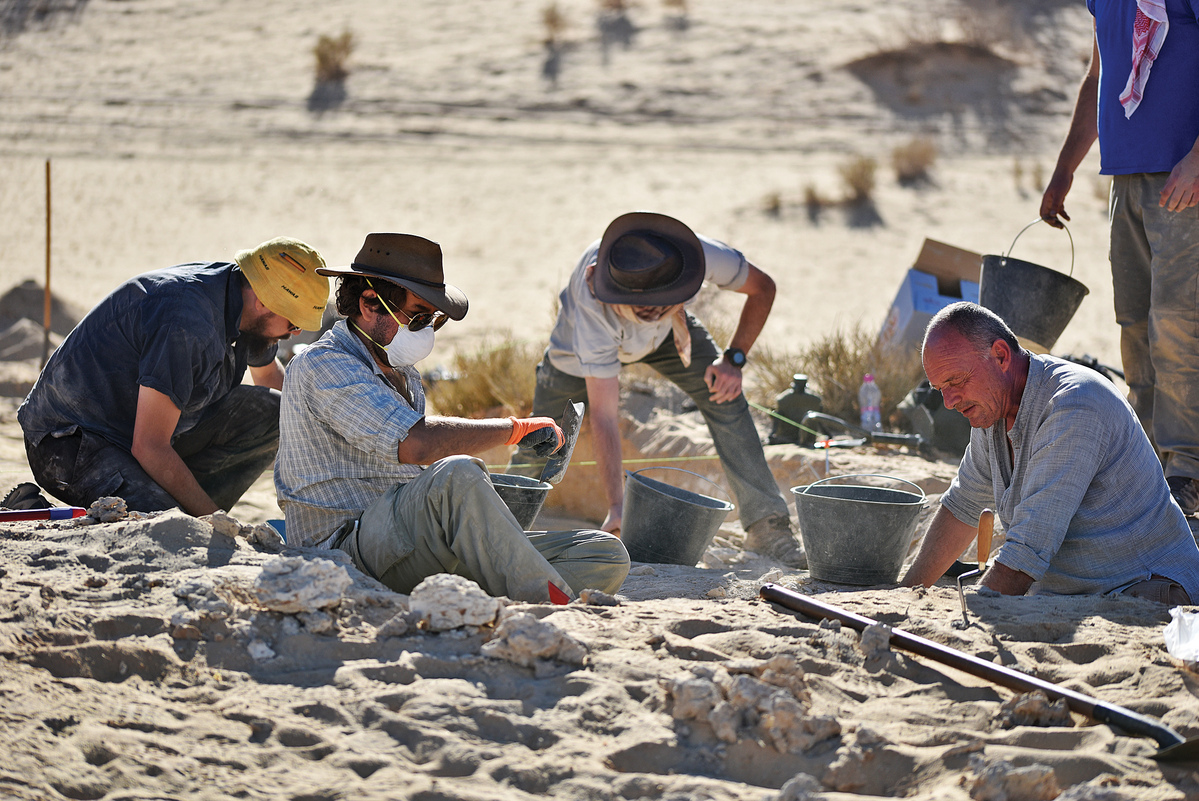

The fossil in Al Wusta was discovered by a team of researchers from the University of Oxford led by archaeologist Huw Groucutt, whose report was published in the journal Nature this week. He had been searching the area for human fossils for 10 years before unearthing a single bone from the middle finger of a Homo sapien.
“It was very clearly a human finger bone - it was instant excitement,” said Groucutt. The bone was found near fossils of hippos and buffalos, suggesting the now arid area was once a vast wetland.
The researchers used computerized tomography - or CT - scanning to confirm the bone was human, followed by a process known as uranium series dating to narrow down its age.
“Many geneticists will say that all of the world’s people come from this migration about 50,000 to 60,000 years ago,” Groucutt said. “Over the last few years that idea has been crumbling.”
Several Chinese archaeologists have long suspected that early humans settled in China between 80,000 to 120,000 years ago.
In 2010, archaeologists Wu Xiujie and Liu Wu of the Chinese Academy of Sciences published a review of hominid archaeological finds in China dating back to the 1970s. They argued that several discoveries - including human teeth found in the Zhiren Cave in Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region - indicate that modern humans existed in China around 100,000 years ago.
However, some found the conclusions dubious as several of the fossils shared characteristics with archaic human species such as Homo erectus.
The Chinese archaeologists made one of their biggest breakthroughs during a 2011 excavation of Fuyan Cave in Hunan province, where they found 47 teeth belonging to modern humans. The teeth were buried underneath stalagmites that were found to be least 80,000 years old, suggesting the fossils were older.
Once again, however, the findings were met with skepticism. The stalagmite used for dating was a short distance from the fossils, and some argued that the area could have been disturbed by geological processes.
“Personally, I am happy with the age and Homo sapien attribution of the fossils in China, but they have been controversial in the field and there have been publications in good journals questioning these finds,” Groucutt said.
“There are people who are very wedded to the idea that no-one left Africa until 50,000 years ago, particularly very prominent voices in genetics. So it is important that people like myself - who do think we left earlier and got to places like China - are really sure. Lots more research needs to be done and the most up-to-date techniques need to be applied,” he said.
































