The shape of China's recovery


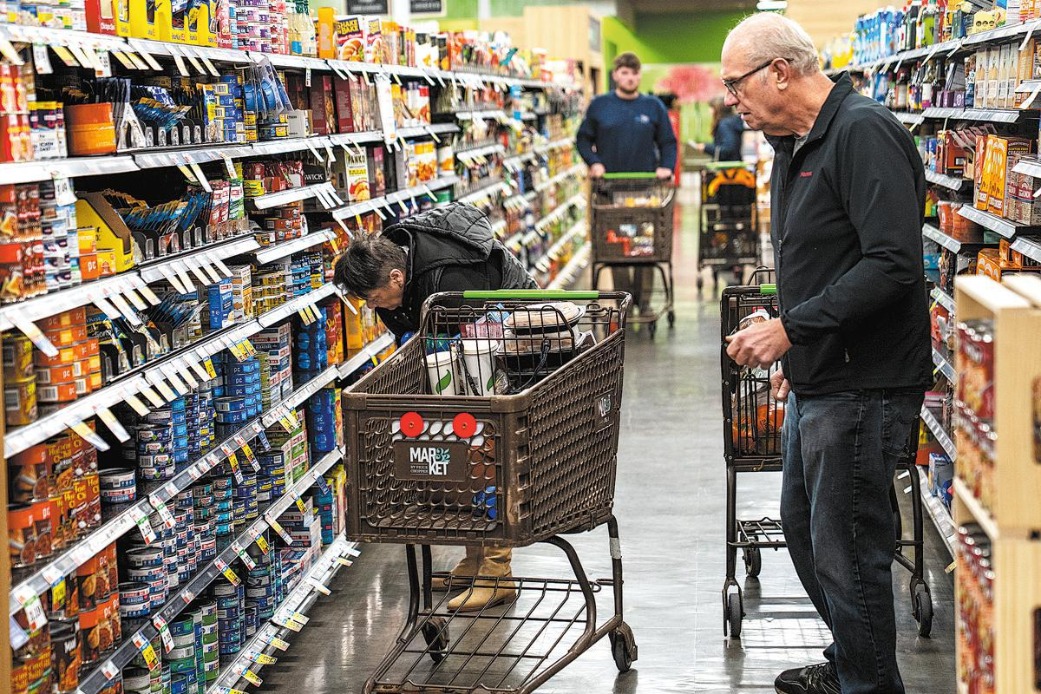
China's economy is on the road to recovery after the COVID-19 shock in the spring of 2020. Negative growth rates in investment, manufacturing activity, and consumption have reversed course and moved into positive territory, and some indicators, such as exports, have even beaten expectations, registering a positive growth rate of more than 10 percent in the third quarter of the year.
How an economy recovers from an economic shock determines how robust its recovery will be. Back in 2009, the Chinese government's 4 trillion yuan ($605 billion) stimulus package following the global financial crisis fueled a credit boom, which inflated the shadow-banking sector and sent debt levels soaring to alarming levels.
To be sure, China's overall response salvaged the economy and maintained impressive growth rates. But as investment flooded into infrastructure projects and housing, and onto the balance sheets of large state-owned enterprises, it created even more economic distortions than there had been before the crisis. Overall productivity growth would remain diminished for the next decade.
This time around, China's recovery is again based on a large stimulus plan, coupled with measures to control the virus so that work and other economic activities can resume. But much of the spending so far has come from the public sector rather than private enterprise. Moreover, recent figures show that China's post-COVID rebound has been led by investments in infrastructure and housing, whereas consumption growth has been sluggish and nowhere near the pre-crisis level.
Even though people are safe going about their normal lives, the service sector is still nowhere near a true recovery. Out of an abundance of caution, people are saving more and going out less. This trend could bode ill not just for China but also for the rest of the world, since it may be an indication of what awaits other economies.
There also are at least three other reasons for concern. First, while China's export figures exceeded expectations this year, they may be more disappointing in the year ahead. In 2020, China acted as a global "supplier of last resort", keeping factories open as they were shut down elsewhere. And because part of China's current growth is led by exports of critical pandemic-related goods (like face masks) to the rest of the world, its positive trade statistics reflect not so much a recovery in global demand as a shift in production to China. This process will reverse whenever global production sites reopen and supply chains start functioning again.
A second concern is that the recovery has triggered a broader structural deterioration, following years of economic reorientation away from exports and investment and toward consumption. There has been some progress in this regard in recent years, but the balance is now shifting back toward investment and trade, as supply leads demand in the process of recovery.
China's macro-level recovery thus masks micro-level challenges. As of the third quarter of 2020, income growth had not recovered, and household disposable income was contracting. Demand for migrant workers had been hit especially hard, and showed no signs of recovery. And the labor force participation rate remained diminished since falling at the onset of the pandemic.
The third cause for concern is that financial risks are looming, and this time they are arising from the real economy. Corporate balance sheets will look substantially worse over time, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. In the first half of 2020, the gap between corporate borrowing and saving rose to unprecedented heights, reaching more than 10 trillion yuan. This would take at least one to two years to resolve even under normal circumstances. If cash flows remain depressed for an extended period, risks of bad debt will rise, especially in the transportation, travel and restaurant sectors. Such debts will pose significant threats to financial institutions as the quality of bank assets (and thus of loan portfolios) deteriorates.
Fortunately, although the government's short-term recovery measures have slowed progress on longer-term reforms, its post-pandemic spending spree is more targeted than last time, and thus unlikely to fuel another credit bubble. Among the most notable features of this package is its emphasis on investments in innovation. In order to build "new infrastructure," the government is redirecting resources from traditional projects to data centers, artificial-intelligence applications, and electric-vehicle charging stations, increasing investment in high-tech manufacturing and services by nearly 10 percent over the course of the year.
Therefore, we should expect a continued commitment to opening up the economy, particularly in financial services. Chinese policymakers recognize that the domestic financial system needs to become more competitive and more closely integrated with Western institutions and corporations amid heightening geopolitical tensions.
Finally, China's recent decision to dispense with a national growth target is a welcome development. With less pressure on local governments to churn out high GDP figures, they can focus instead on boosting employment, improving people's livelihoods, strengthening food and energy security, and creating opportunities for small and medium-sized business.
China is a decade wiser than it was when it encountered its first major economic challenge of the post-1978 era of reform and opening-up. Having matured as an economy and grown more patient, China is less eager to achieve short-term gains, and more invested in creating opportunities for its people over the long term. The recovery may be slow, but it will follow a path that is smoother and more secure than the route taken last time.
The views don't necessarily represent those of China Daily.
The author, a professor of Economics at the London School of Economics, is a World Economic Forum Young Global Leader. Project Syndicate